
How to Align SDG Data Governance with ISO 14064

Dec 5, 2025
How accounting firms can map SDG indicators to ISO 14064, centralise evidence, automate carbon accounting and produce audit‑ready sustainability reports.
Aligning SDG data governance with ISO 14064 can simplify sustainability reporting, reduce errors, and help accounting firms meet compliance requirements while building client trust. Here's how:
SDG Data Governance: Focuses on managing and reporting data related to the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
ISO 14064: Provides a framework for greenhouse gas (GHG) accounting and verification, covering emissions measurement, monitoring, and reporting.
Why This Matters:
Streamline Processes: Linking SDG indicators to ISO 14064 emissions categories avoids duplicated efforts and ensures consistency.
Audit Readiness: Establish clear audit trails by integrating financial and sustainability data.
Regulatory Compliance: Align with UK standards like SECR, UK SRS, and ISSB reporting.
Revenue Opportunities: Offer sustainability services to clients, turning compliance into a business advantage.
Key Steps:
Map SDG Indicators to ISO 14064: Connect SDG metrics (e.g., energy use, waste management) to relevant GHG emission scopes.
Build a Governance Framework: Define roles, policies, and centralise data for reliable reporting.
Generate Audit-Ready Reports: Use tools like neoeco to automate data mapping, ensure accuracy, and meet compliance standards.
By integrating these frameworks, accounting firms can efficiently manage sustainability reporting, reduce compliance risks, and strengthen client relationships.
Introduction to ISO 14064 - Greenhouse Gas Accounting and Verification
Step 1: Map SDG Data Governance to ISO 14064 Standards
Start by aligning SDG data governance with ISO 14064 standards to ensure consistent sustainability data flows smoothly from financial records to compliance reports. Let’s break down ISO 14064’s main elements to understand how this mapping works.
ISO 14064 Key Requirements
ISO 14064 is divided into three parts, each focusing on different aspects of greenhouse gas (GHG) accounting and verification. These components are crucial for creating a governance framework that supports both SDG reporting and carbon compliance.
Part 1 deals with organisational GHG inventories. It involves identifying emission sources, quantifying Scopes 1, 2, and 3 emissions, and setting a base year. This is the foundation for corporate carbon reporting in the UK.
Part 2 focuses on project-level GHG reductions or removals. While this is less relevant for most accounting clients, it’s essential for those involved in carbon offset projects or renewable energy initiatives that require verification.
Part 3 outlines the verification and validation processes. It sets principles and requirements for independent assurance of GHG statements, which is increasingly demanded by regulators, investors, and stakeholders. As external auditors intensify their scrutiny of carbon data, ensuring your data governance aligns with these verification standards from the start is critical.
ISO 14064 demands thorough documentation of methodologies, data sources, assumptions, and calculations. Every emission figure must be traceable to verifiable evidence, such as financial records, utility bills, or supplier data.
Link SDG Indicators with ISO 14064 Emissions Categories
Once the ISO 14064 framework is clear, the next step is to align specific SDG indicators with the appropriate emission scopes. While SDG indicators often overlap with carbon accounting requirements, they’re not typically structured to match ISO 14064 directly. Bridging this gap requires careful mapping of SDG metrics to the relevant emissions categories.
SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) tracks energy consumption and renewable energy usage. These indicators align with Scope 2 emissions, as purchased electricity is a major component of this category. Data on renewable energy adoption under SDG 7 can directly inform Scope 2 calculations, ensuring consistency and reducing duplicated effort.
SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) includes metrics for waste generation, material efficiency, and circular economy initiatives. Waste disposal and treatment fall under Scope 3, specifically Category 5 (Waste generated in operations). Linking SDG 12 waste targets to Scope 3 ensures resource efficiency and compliance are addressed together.
SDG 13 (Climate Action) is closely tied to an organisation’s overall GHG inventory. Climate-related targets, emission reduction goals, and carbon intensity metrics under SDG 13 should align with ISO 14064’s broader GHG reporting framework.
The goal is to avoid treating these frameworks as separate exercises. For instance, if a client tracks energy efficiency improvements for SDG reporting, that same data should update their Scope 2 emissions. Similarly, business travel data for SDG 13 should feed into Scope 3 Category 6 (Business travel). This integrated approach prevents conflicting figures in different reports - a major red flag for auditors.
For firms managing multiple clients, consistency in this mapping process is essential. Standardised templates that connect SDG indicators with ISO 14064 categories allow for a rigorous approach across all clients while accommodating sector-specific needs.
Use Automation Tools Like neoeco for Efficient Mapping
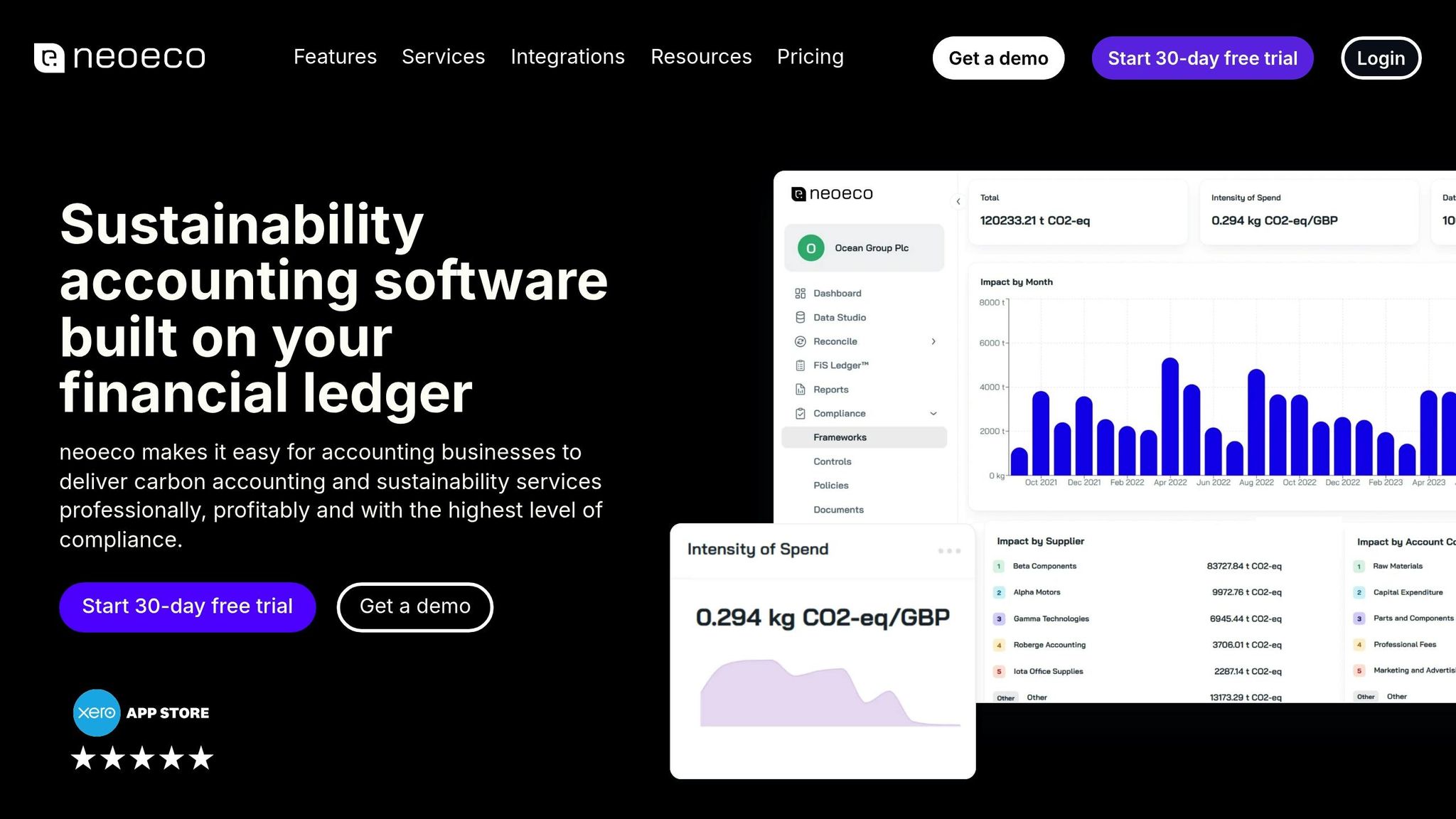
Manual mapping is time-consuming and prone to errors, especially when dealing with multiple clients, varied transaction types, and complex reporting requirements. Automation tools like neoeco can streamline this process.
neoeco integrates directly with financial platforms like Xero, Sage, and QuickBooks, automatically mapping transactions to recognised emissions categories under both the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHGP) and ISO 14064. For example:
Fuel purchases are categorised under Scope 1 with the correct emission factor.
Electricity bills are assigned to Scope 2.
Office supplies, courier services, and professional fees are allocated to the relevant Scope 3 categories.
This automation eliminates the need for spreadsheets and manual data conversions, ensuring carbon data is grounded in financial transactions that have already been reconciled and verified.
The tool also ensures consistency across clients by applying standard methodologies aligned with ISO 14064. When emission factors or reporting requirements change, updates are applied automatically, reducing the risk of outdated data and inconsistencies that could undermine audit readiness.
For firms aiming to align sustainability reporting with ISSB reporting requirements, neoeco’s integration with financial data provides a strong foundation. By using the same ledger data for both financial and carbon accounts, firms can demonstrate the reliability and accuracy that regulators and auditors demand.
Additionally, neoeco’s evidence hub allows firms to store all supporting documentation - utility bills, supplier invoices, and policy documents - alongside transaction data. This makes it easy to provide auditors with clear links between financial transactions, emission calculations, and supporting evidence. Achieving this level of organisation with spreadsheets is challenging, but it’s crucial for ISO 14064 verification.
Step 2: Build a Data Governance Framework
After mapping SDG indicators to ISO 14064 emissions categories, the next step is to create a framework that ensures your data is reliable, consistent, and ready for audits. This framework should outline clear roles, define how data flows through your systems, and specify where all supporting evidence is stored. Without proper governance, even the most thorough mapping exercise can fall apart during audits. A solid governance framework ensures accurate data translates into audit-ready reports.
Set Clear Policies and Procedures
With your mapping in place, the next task is to document clear policies to manage data flow. These policies should address both SDG indicators and ISO 14064 requirements while also adhering to UK-specific frameworks like SECR (Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting) and the UK Sustainability Reporting Standard (UK SRS).
Assigning roles and responsibilities is key. For example, one team member could oversee data collection, another could verify calculations, and a senior team member could approve reports before submission. This separation of duties reduces errors and ensures accountability - both critical for ISO 14064 verification.
Your policies should also specify data sources and methodologies. For instance, detail the method used for Scope 2 calculations and the emission factors applied. Defining these elements helps maintain consistency and ensures a unified approach across all client reports.
Every calculation should be traceable back to its source, whether it's a utility bill, fuel receipt, or supplier invoice. This traceability is crucial for verification. For firms handling multiple clients, standardised policies and adaptable templates can help maintain consistency across all reports.
Maintain Data Accuracy and Consistency
Accuracy and consistency are non-negotiable for SDG reporting and ISO 14064 compliance. Integrating financial data directly with sustainability reporting ensures carbon calculations are based on reconciled financial records, reducing the risk of errors from manual data entry or spreadsheets.
To achieve this, neoeco integrates with financial platforms to automatically match transactions to the appropriate emissions categories. This automation eliminates manual conversions and grounds each emission figure in verified financial data.
Consistency is further reinforced by using standardised approaches and conducting regular data validation. Tools that apply uniform logic across all clients ensure your practice maintains the same high standards, regardless of the scale or complexity of the engagement.
Centralise Evidence and Documentation
ISO 14064 verification depends on the ability to provide well-organised evidence for every emission figure. Scattered spreadsheets can complicate this process, so centralising all compliance files is essential.
A dedicated policy and evidence hub can serve as a central repository for utility bills, supplier invoices, calculation methodologies, and audit trail records. This makes it easy to quickly retrieve the required documentation when auditors request evidence for a specific emission source.
neoeco's Policy & Evidence Hub simplifies this process by linking supporting documents directly to the transactions that generated the emissions. For example, an electricity bill can be stored alongside the related Scope 2 emissions data, complete with an audit trail showing who entered the data, when it was verified, and the emission factors used. This level of organisation makes audits more efficient by providing immediate access to evidence.
Audit controls, like checklists that track completed, pending, and review-ready items, can further streamline the process. Providing auditors with secure, direct access to reports and evidence via the platform not only saves time but also reduces costs.
When centralising sensitive sustainability data, security and compliance are critical. Choosing platforms that meet SOC 2 and GDPR standards ensures client information is protected while meeting regulatory requirements. A centralised system that supports multiple reporting frameworks - such as GHGP, ISO 14064, SECR, and UK SRS - also minimises duplication, reduces errors, and creates a single source of truth for both auditors and clients.
Step 3: Prepare Audit-Ready Reports Aligned with ISO 14064
Once you’ve established a solid data governance system, it’s time to transform that data into audit-ready reports. This step focuses on converting your organised data and centralised evidence into professional outputs that meet compliance standards. The aim is to create reports that highlight accuracy, traceability, and adherence to recognised frameworks. With automated reporting, you can easily track progress and simplify the audit process.
Generate Compliance-Ready Reports
Creating reports that comply with SECR, UK SRS, and ASRS 2 requirements becomes much easier when your data is well-structured and governed. Yet, for many accounting firms, the real hurdle lies in turning raw emissions data into regulatory-compliant reports.
This is where neoeco steps in. Its report builder is designed specifically for accounting firms, integrating financial data seamlessly to produce reports in just minutes. It applies the correct methodologies under GHGP and ISO 14064, ensuring compliance without the hassle.
The platform includes templates tailored for SECR, UK SRS, and ASRS 2, so your reports meet the precise disclosure requirements of each framework. For firms working across different jurisdictions, this flexibility means you can switch between frameworks without overhauling your entire reporting process.
You can also customise reports with your firm’s branding - logos, colours, and all - giving your clients polished documents that reflect your professional standards. Instead of generic outputs, clients receive reports that underscore the quality of your advisory services.
From a single dataset, you can generate multiple reports tailored for auditors, boards, or other stakeholders, all without duplicating effort.
Track and Review Progress
Before finalising reports, it’s crucial to confirm that all necessary data is complete, accurate, and backed by evidence. Real-time dashboards and live checklists help identify any missing information and ensure everything is in order.
neoeco's audit-ready controls include a live checklist that flags incomplete data or missing documentation. For example, if a client hasn’t provided their Scope 2 electricity data or uploaded a supporting invoice, the system will alert you immediately.
Dashboards provide a clear view of emissions trends and intensity, offering insights that go beyond compliance. If a client’s emissions rise significantly compared to a previous period, you can investigate the cause and recommend strategies for improvement.
For firms managing multiple clients, these dashboards are invaluable. They give you a snapshot of progress across your entire portfolio, helping you quickly identify which clients are ready for audits and which need more attention. This reduces the risk of missed deadlines and improves efficiency during busy reporting times. Plus, stakeholders can securely access real-time data through the dashboard, promoting transparency.
With progress tracking sorted, the next step is to ensure a smooth external audit process.
Facilitate External Audits
ISO 14064 verification requires external auditors to review your emissions data and supporting evidence. Making this process straightforward not only saves time but also reduces costs by ensuring auditors have secure, organised access to everything they need.
neoeco's easy auditor access feature allows you to invite auditors to review data and documentation securely. The platform ensures that all verified data and supporting evidence are easily accessible, speeding up the verification process.
At the heart of this is the Policy & Evidence Hub, which links supporting documents directly to relevant transactions and emissions data. For example, when verifying Scope 1 emissions from company vehicles, auditors can instantly access fuel receipts, mileage logs, and emission factors - all in one place.
For firms interested in expanding into sustainability assurance services, having a platform that supports both reporting and audit preparation is a game-changer. It positions your firm as a trusted provider of ISSB reporting and ISO 14064 verification, opening up new opportunities and strengthening client relationships.
Lastly, prioritising robust data security is essential. With regulatory requirements for ESG disclosures growing, ensuring sensitive client data remains protected throughout the audit process is non-negotiable. Platforms like neoeco help you maintain this critical level of security while managing sustainability data effectively.
Conclusion
Bringing SDG data governance in line with ISO 14064 lays the groundwork for accurate, efficient, and reliable sustainability reporting. By aligning SDG indicators with ISO 14064 emissions categories, implementing clear governance frameworks, and delivering audit-ready reports, your firm positions itself as a leader in a field that's becoming increasingly crucial. These steps not only ensure compliance but also turn it into a strategic advantage.
Key Takeaways
The outlined three-step approach offers accounting firms a practical way to integrate sustainability into their services. By mapping SDG indicators to ISO 14064, you establish a consistent and auditable emissions reporting framework that aligns with recognised standards like GHGP, SECR, and UK SRS. A solid data governance framework - with clear policies, centralised documentation, and routine data quality checks - minimises reporting errors and saves valuable time during peak reporting periods. Producing compliance-ready reports ensures your governance efforts translate into trusted outputs for clients, auditors, and stakeholders.
This approach goes beyond compliance, unlocking new revenue opportunities. Firms that provide ISSB reporting and ISO 14064 verification services stand out in a competitive market. With clients increasingly expecting sustainability advice alongside traditional financial services, those who meet this demand can retain current clients and attract new ones.
Streamlining compliance processes also reduces manual workload, allowing your team to focus on delivering strategic sustainability insights. This includes helping clients interpret emissions data, identify reduction opportunities, and prepare for future regulations. Shifting from compliance to advisory strengthens client relationships and positions your firm as a trusted partner.
Adopting tools that support future compliance and growth builds on these foundations.
Future-Proof Your Firm with Tools Like neoeco
Relying on outdated manual processes and spreadsheets limits efficiency. As frameworks like UK SRS and ASRS 2 evolve, firms need systems that adapt automatically to new standards.
neoeco offers a single platform for managing various reporting frameworks, simplifying transitions to new standards without requiring additional training. It directly maps financial data to recognised emissions categories under GHGP, ISO 14064, and national frameworks, eliminating the need for spreadsheets and manual data conversions.
For firms venturing into sustainability services, neoeco provides a professional, compliant, and profitable carbon accounting solution. It positions sustainability as an integral part of your service offering, keeping you ahead of market expectations.
With audit-ready controls and a centralised evidence hub, external verification becomes quicker and more straightforward. Features like smart matching link financial transactions to the correct carbon data with speed and accuracy, ensuring the data integrity necessary for compliance. The platform's intuitive report builder produces clear, professional outputs that reflect your firm’s high standards.
Whether you're starting with carbon accounting or expanding into broader sustainability assurance, adopting tools that integrate with trusted financial systems like Xero, Sage, or QuickBooks makes the transition seamless. By leveraging the financial data you already rely on, you ensure accuracy while unlocking new opportunities.
The firms that will thrive in the coming years are those that treat sustainability reporting as a core accounting function rather than an optional service. By combining robust SDG data governance with ISO 14064 standards, your firm not only meets today’s compliance needs but is also ready for the sustainability challenges of the future.
FAQs
How can accounting firms align SDG data governance with ISO 14064 to improve compliance and audit readiness?
Aligning sustainability data governance with ISO 14064 allows accounting firms to ensure their sustainability reports are precise and adhere to established standards. By following a structured approach to managing carbon data, firms can simplify their workflows, minimise mistakes, and confidently comply with regulatory demands.
Tools like neoeco offer automation capabilities, mapping financial transactions to emissions categories under ISO 14064 and similar frameworks. This removes the need for manual data entry, ensuring that calculations and assumptions are thoroughly documented. The result? Audit-ready reports that stand up to regulatory review. By leveraging dependable, finance-grade carbon data, firms not only strengthen their reputation but also position themselves to meet the growing demand for sustainability-focused services.
How can automation tools like neoeco help align SDG data governance with ISO 14064 standards?
Automation tools like neoeco make it easier to align SDG data governance with ISO 14064 by automatically matching financial transactions to established emissions categories. This ensures adherence to global standards like the GHGP and ISO 14064, as well as national frameworks such as SECR and UK SRS.
By removing the hassle of spreadsheets and manual data processing, neoeco delivers precise, finance-grade carbon data along with audit-ready reports. This streamlines the process, saves valuable time, and boosts the reliability of sustainability reports, enabling businesses to confidently provide professional and compliant carbon accounting services.
How can accounting firms align SDG data governance with ISO 14064 to unlock new revenue streams in sustainability services?
Accounting firms can connect Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) data governance with the ISO 14064 standard by embedding advanced carbon accounting practices into their services. This approach ensures adherence to globally recognised frameworks while enabling the delivery of precise, audit-ready sustainability reports.
Using tools like neoeco, which links financial transactions directly to emissions categories outlined in ISO 14064, firms can simplify reporting. This eliminates the need for spreadsheets or manual data handling, improving efficiency and accuracy. Beyond operational benefits, this positions your firm as a reliable partner for clients needing high-quality, finance-grade sustainability services. Expanding into this domain offers opportunities to attract new clients, strengthen existing relationships, and tap into the growing demand for sustainability-focused solutions.
