
Audit Trails for Materiality Documentation Updates

Dec 17, 2025
Audit trails make materiality documentation verifiable: track who, when and why, centralise evidence, manage versions and automate reporting.
Audit trails are essential for managing materiality documentation updates in sustainability reporting. They provide a chronological record of changes, ensuring transparency, accountability, and compliance with regulatory standards like UK SRS, SECR, and ISSB. Without them, organisations risk compliance failures and credibility issues.
Key points:
Audit trails track who made changes, when, and why.
They simplify verification for auditors and ensure consistency.
Regulatory frameworks demand clear records of materiality decisions.
Tools like neoeco automate tracking and integrate data for efficiency.
How Do I Confirm Audit Documentation Accuracy?
Regulatory Standards for Materiality Documentation
Sustainability reporting regulations have grown stricter, both within the UK and internationally. Organisations are now required to not only define what they consider material but also explain the processes behind these decisions and how they are revised over time. Transparency is at the heart of these requirements, with regulators insisting on detailed audit trails. These trails are a cornerstone of compliance, ensuring that organisations can substantiate their sustainability data. Let’s look at how UK and international standards enforce these expectations.
UK SRS and SECR Requirements
In the UK, the Sustainability Reporting Standard (UK SRS) and Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) regulations demand robust and audit-ready controls. Organisations must create a centralised evidence hub to securely store all compliance-related files. This ensures sustainability data is not only accurate but also readily verifiable. Without such audit trails, auditors face challenges in confirming compliance.
For accounting firms managing multiple clients, tools like neoeco simplify the process by offering platforms with built-in audit-ready controls and secure data storage. This eliminates the need for manual processes, making it easier to align with UK SRS and SECR requirements.
International Standards: IFRS S1/S2 and ISO 14064
Internationally, the emphasis on audit trails is equally strong. The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) has introduced IFRS S1 and S2 standards, which compel organisations to disclose how they identify and evaluate material sustainability issues. These standards require detailed records of decision-making processes, including the rationale behind decisions and any subsequent updates.
Similarly, ISO 14064, the global standard for greenhouse gas accounting, mandates that organisations maintain meticulous records of materiality thresholds used in emissions reporting. When these assessments are updated, organisations must clearly document the timing, reasoning, and individuals responsible for the changes. Such requirements underline the necessity of transparency and traceability, particularly for organisations operating across multiple jurisdictions. Audit trails are not just a regulatory demand - they are a practical tool for maintaining accountability and consistency in sustainability reporting.
How to Create and Maintain Audit Trails
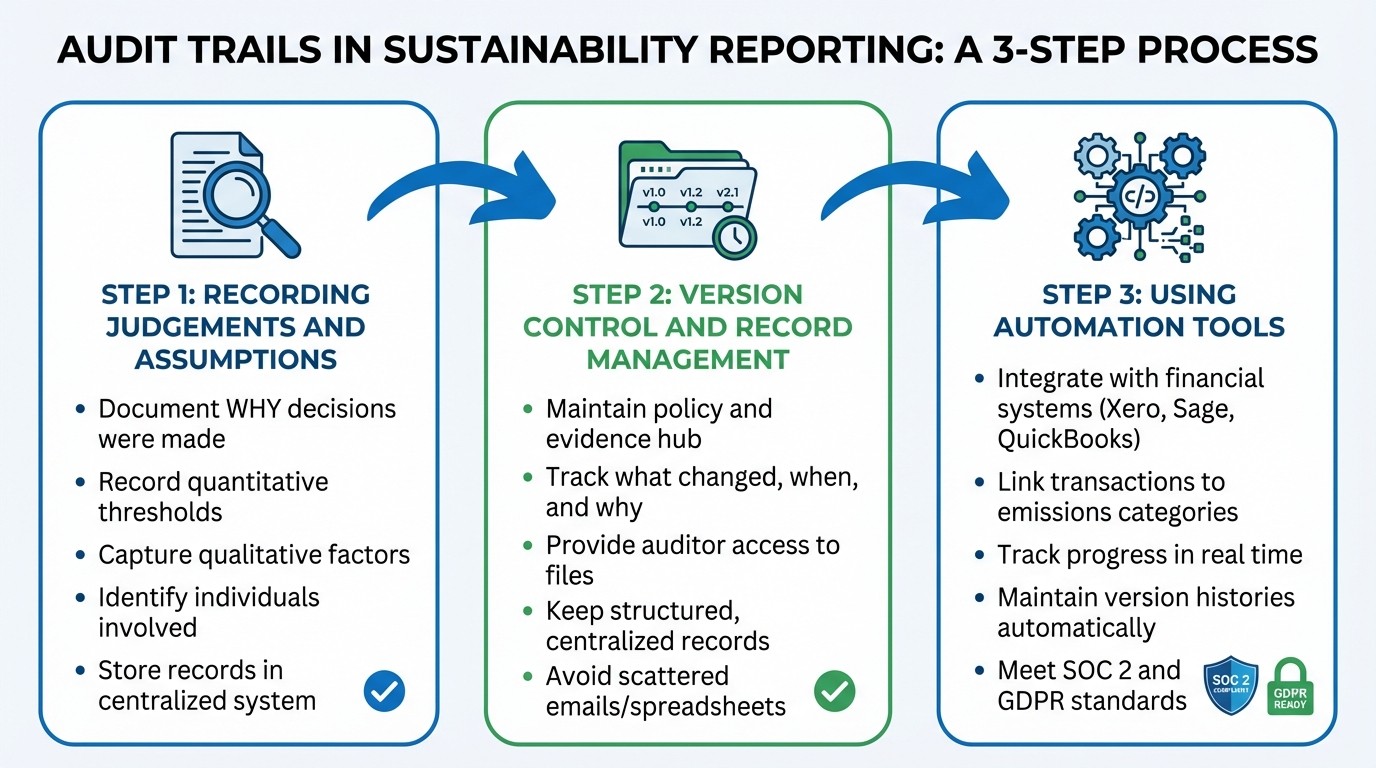
Three Essential Steps for Creating Effective Audit Trails in Sustainability Reporting
Creating effective audit trails for materiality documentation isn’t just about meeting requirements - it’s about building a system that can withstand scrutiny. With the right approach, audit trails become clear and manageable. Here’s how to record decisions, manage versions, and utilise automation to ensure transparency.
Recording Judgements and Assumptions
Transparent documentation starts with capturing the reasoning behind every decision. Each materiality assessment involves professional judgement, so it’s essential to document why a decision was made, not just what the decision was. For example, if a sustainability issue is deemed material, record the quantitative thresholds, qualitative factors, and the individuals involved in the decision-making process. Store these records securely in a centralised system to maintain consistency across clients. This not only helps when assessments are challenged or updated but also ensures you have clear evidence to back your decisions.
Version Control and Record Management
Version control is key to staying organised and accountable. When materiality thresholds shift - whether due to regulatory changes, stakeholder input, or internal developments - maintain a policy and evidence hub. This hub should securely house all compliance files, making it easy to track what changed, when, and why. By keeping these records in a structured and centralised system, auditors can trace the evolution of materiality assessments without sifting through scattered emails or spreadsheets. Providing auditors with controlled access to these files simplifies the verification process, allowing them to review reports and evidence directly within the system. Automating these processes can make record management even more efficient and transparent.
Using Automation Tools for Audit Trails
Automation tools can fill the gaps left by manual processes, ensuring every change is recorded without errors. Manual audit trails often risk inconsistencies, but tools that integrate with financial systems - such as Xero, Sage, or QuickBooks - offer a more reliable solution. Platforms like neoeco build sustainability data directly from existing financial records, automatically linking transactions to emissions categories under frameworks like GHGP and ISO 14064. This creates a seamless connection between source data and reported outcomes. The platform also tracks progress in real time and securely stores supporting documentation, meeting SOC 2 and GDPR standards. By automating data matching and maintaining version histories, these tools reduce manual workload while ensuring every update is traceable. For firms managing multiple clients, this approach provides both efficiency and peace of mind - without requiring teams to become experts in sustainability overnight.
Common Challenges and Practical Solutions
Maintaining clear and reliable audit trails is essential, but firms often encounter challenges in ensuring consistency and adopting the right technology.
Subjectivity and Consistency Issues
Materiality assessments rely heavily on professional judgement, which can lead to inconsistent thresholds and varying interpretations across different periods or clients - especially when clear guidelines are absent. These inconsistencies can cause problems during audit reviews, as variations may be difficult to justify. To tackle this, firms should adopt structured frameworks that outline how materiality decisions are made and documented. Using policy templates can help standardise these processes, ensuring every assessment follows a consistent logic and set of criteria. Such frameworks not only improve consistency but also strengthen audit trails. Addressing these human factors is just as important as resolving the technological challenges tied to audit trail management.
Technology and Process Gaps
Relying on manual processes or spreadsheet-based systems often leads to inefficiencies, data inaccuracies, and poor version control. The lack of integration between financial ledgers and sustainability systems further complicates matters, creating opportunities for data to be lost or misinterpreted. When data is scattered across disconnected spreadsheets, tracking changes becomes nearly impossible. Integrated software solutions, such as those compatible with platforms like Xero, Sage, or QuickBooks, can solve these issues by centralising data and automating updates. Tools like neoeco link transactions directly to emissions categories under frameworks like GHGP, SECR, and UK SRS, ensuring a seamless audit trail from the original data to the final report. This integration not only eliminates manual errors but also ensures that every change is recorded and easy to trace. Using a single, integrated system boosts efficiency and inspires greater confidence in regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Audit trails play a critical role in meeting regulatory requirements, ensuring transparency with clients, and improving operational processes. Without well-documented records of materiality decisions and their updates, firms risk non-compliance and struggle to prove accountability.
Key Takeaways for Accounting Firms
The most forward-thinking firms see audit trails not just as a compliance necessity but as a chance to gain a strategic edge. Using structured frameworks helps maintain consistency in materiality assessments, while integrated software solutions minimise the risk of manual errors. For example, platforms like neoeco show how sustainability accounting can seamlessly connect with financial ledgers, creating a complete audit trail from raw data to final reports.
Streamlined, audit-ready controls make reviews smoother. A centralised hub for policies and evidence ensures compliance files are securely stored and always accessible. This setup not only simplifies auditor access but also demonstrates accountability. Standardised templates further support consistency and ensure documentation meets top-tier standards.
FAQs
Why are audit trails important for maintaining compliance in sustainability reporting?
Audit trails are crucial for meeting sustainability reporting standards. They serve as a clear record of calculations, assumptions, and updates, ensuring clarity and accountability at every step of the reporting process.
With detailed audit trails in place, organisations can prove the reliability of their data and confirm their reports align with regulatory expectations. This approach not only helps them handle scrutiny from auditors and regulators but also strengthens trust with stakeholders by highlighting a dedication to precise and dependable reporting.
How can automation tools enhance the efficiency of audit trails?
Automation tools simplify the process of maintaining audit trails by capturing and securely storing data, calculations, and assumptions as they happen. This not only cuts down on manual work but also reduces the risk of errors, ensuring every action is traceable and ready for compliance reviews.
By replacing spreadsheets and manual data entry, these tools enhance precision and efficiency. They free up valuable time, enabling firms to concentrate on producing reliable, audit-ready documentation with assurance.
What are the common challenges in maintaining reliable audit trails for materiality documentation?
One of the hurdles in maintaining reliable audit trails is the reliance on manual data collection. This approach often leads to errors, incomplete records, and a lack of clarity. Additionally, firms might find it tough to consistently document assumptions and calculations while also safeguarding data and ensuring traceability.
Automated systems offer a practical solution by reducing manual errors, improving data accuracy, and generating documentation that's ready for audits. These systems streamline compliance efforts, save valuable time, and ensure precision when updating materiality assessments.
